In the glass manufacturing industry, ceramic fiber modules have emerged as a key insulation technology. They deliver compelling benefits: significant energy savings, improved temperature uniformity, longer furnace life, and supporting ultra-low emissions. These modules offer a practical way for glass plants to modernize. They help to lower operating costs and meet stricter environmental standards.
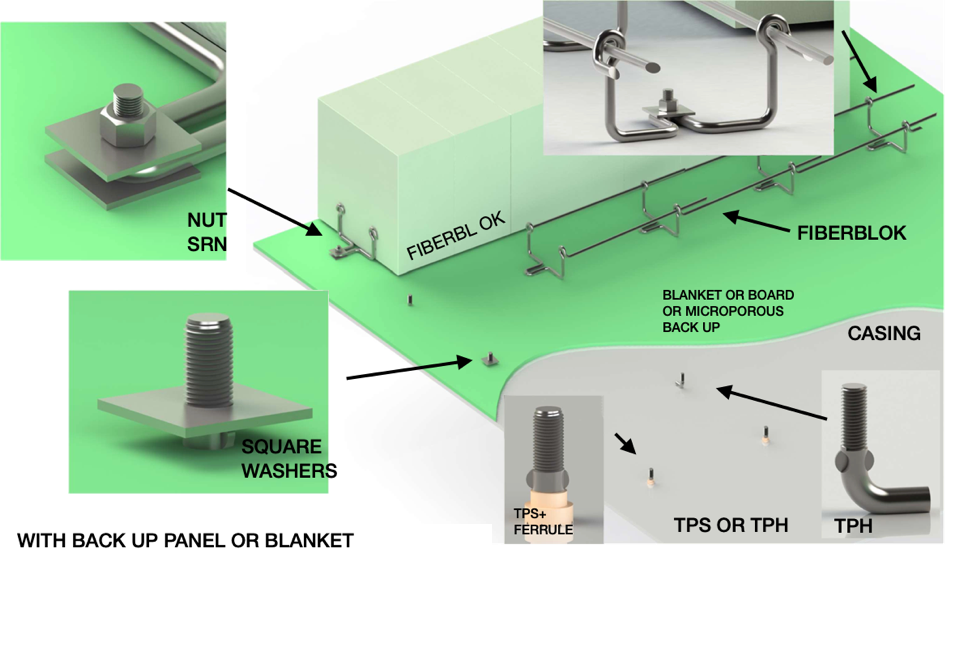
Major Energy Savings: Ceramic fiber modules reduce thermal losses due to their extremely low thermal conductivity and low heat storage. By replacing heavier refractory linings in tempering furnaces, module-based insulation can cut energy consumption by more than 30%. This helps plants reduce fuel or electricity costs.
Rapid Thermal Response: With low thermal mass, ceramic fiber modules accelerate heating and cooling cycles. This reduces downtime and increases furnace throughput.
Temperature Stability and Uniformity: When used in furnace roofs or side-walls, modules help maintain temperature variations within ±2–3 °C. This reduces glass stress defects and significantly improves product consistency.
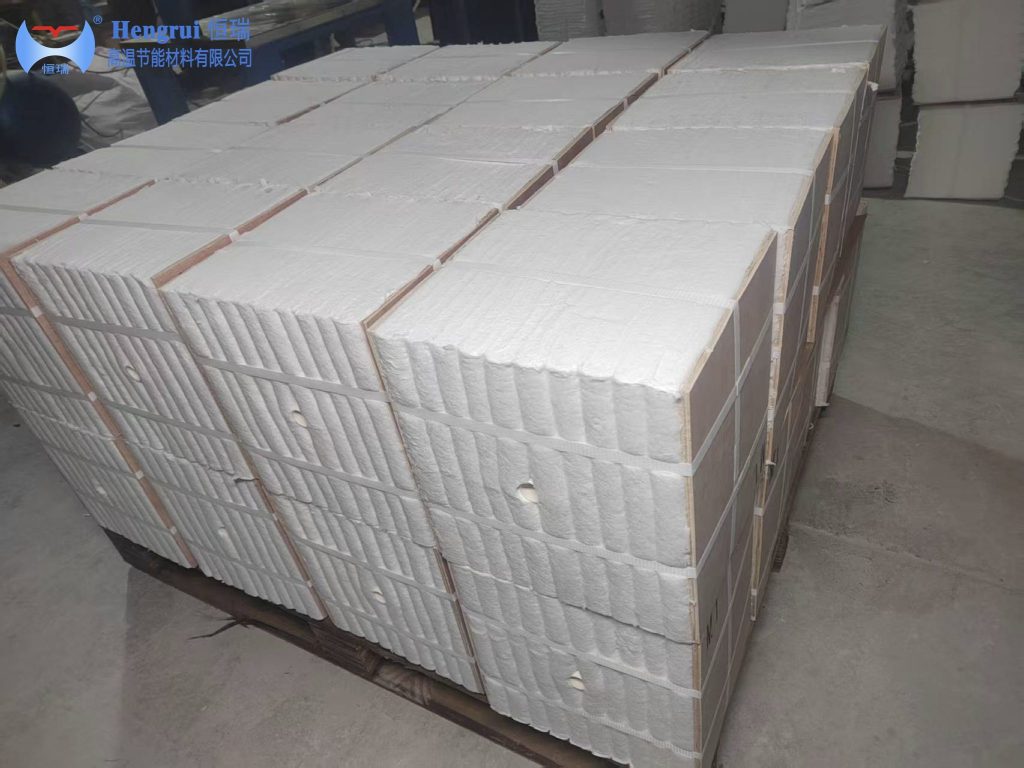

Improved Temperature Sealing: In annealing lehrs, modules act as a robust barrier against air infiltration. Their tight fit stabilizes cooling profiles, minimizing thermal shock and reducing the cracking rate of glass products.
Longer Furnace Life: Compared to traditional dense bricks, ceramic fiber modules produce less structural stress. Their elasticity helps absorb thermal expansion and contraction, reducing the risk of lining failure and increasing maintenance intervals.
Reduced Emissions: When combined with ceramic filtration systems, fiber modules support efficient particulate and NOₓ control. This helps glass manufacturers achieve ultra-low emission standards.
High-Temperature Capability: Modules are available in a variety of classifications. A common grade is the 1260 °C module, with higher-grade high-alumina modules (around 1360 °C) used for demanding zones.
Low Thermal Conductivity: High-purity modules achieve excellent insulation performance, cutting heat flux through the furnace lining.
Low Shrinkage and Dimensional Stability: Quality modules show minimal permanent linear change after repeated high-temperature cycles. This helps maintain long-term structural integrity.
Flexible Anchoring & Fast Installation: Pre-compressed modules with built-in anchoring systems ensure tight joints. They reduce heat loss and enable faster furnace construction or retrofitting.
Lightweight Construction: With bulk densities typically between 160–220 kg/m³, ceramic fiber modules reduce furnace shell loads. They simplify installation, especially for large refractory structures.
Retrofitting Existing Furnaces
Existing tempering, melting, or annealing furnaces can be upgraded by replacing traditional refractory linings with ceramic fiber modules. This delivers immediate improvements in energy efficiency and thermal responsiveness.
Multi-Layer Insulation Design
Many advanced furnace designs combine:
Smart Thermal Monitoring
Integrating sensors into module linings allows real-time thermal analysis. It enables early detection of hot spots and predictive maintenance. This reduces downtime and preserves insulation performance.
Sustainable Innovation
New aerogel–fiber composite modules are emerging. Their ultra-low thermal conductivity supports even higher energy savings and aligns with green manufacturing directives.
Chemical Sensitivity: In atmospheres with aggressive vapors or corrosive gases, fiber modules may degrade over time. In such cases, they should be positioned as backup insulation rather than the working surface.
Mechanical Strength: Ceramic fiber modules are not suitable for high-impact or abrasive zones. Protective layers may be required in loading, batch-charging, or flame-impingement areas.
Cost & Logistics: Although modules significantly reduce long-term operating costs, initial investment and anchoring hardware must be properly evaluated in project planning.
Ceramic fiber modules provide a modern, high-efficiency insulation solution for the glass industry. Their low thermal conductivity, rapid thermal response, structural flexibility, and compatibility with clean-air systems make them an excellent choice for glass manufacturers. They are aiming for higher productivity and lower emissions.
Whether upgrading an existing furnace or designing a new system, ceramic fiber modules offer a future-ready approach. This approach leads to energy-saving, stable, and sustainable glass production.