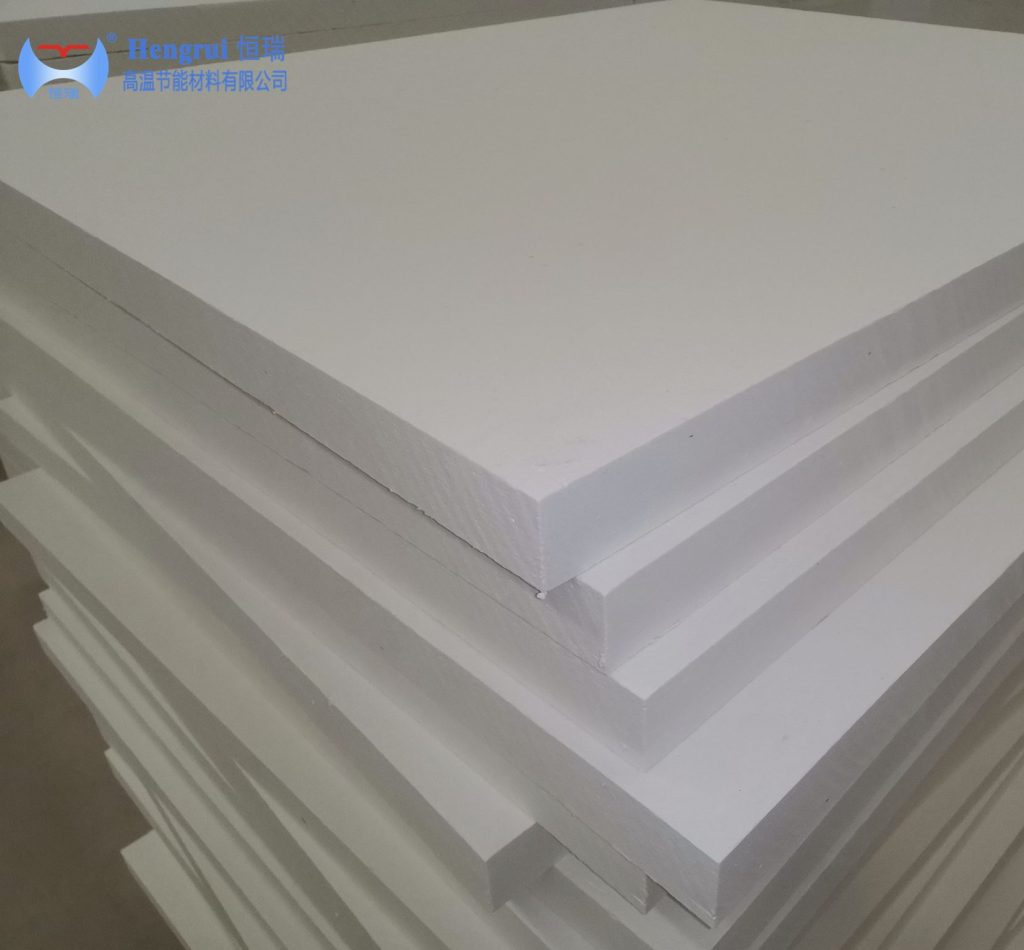
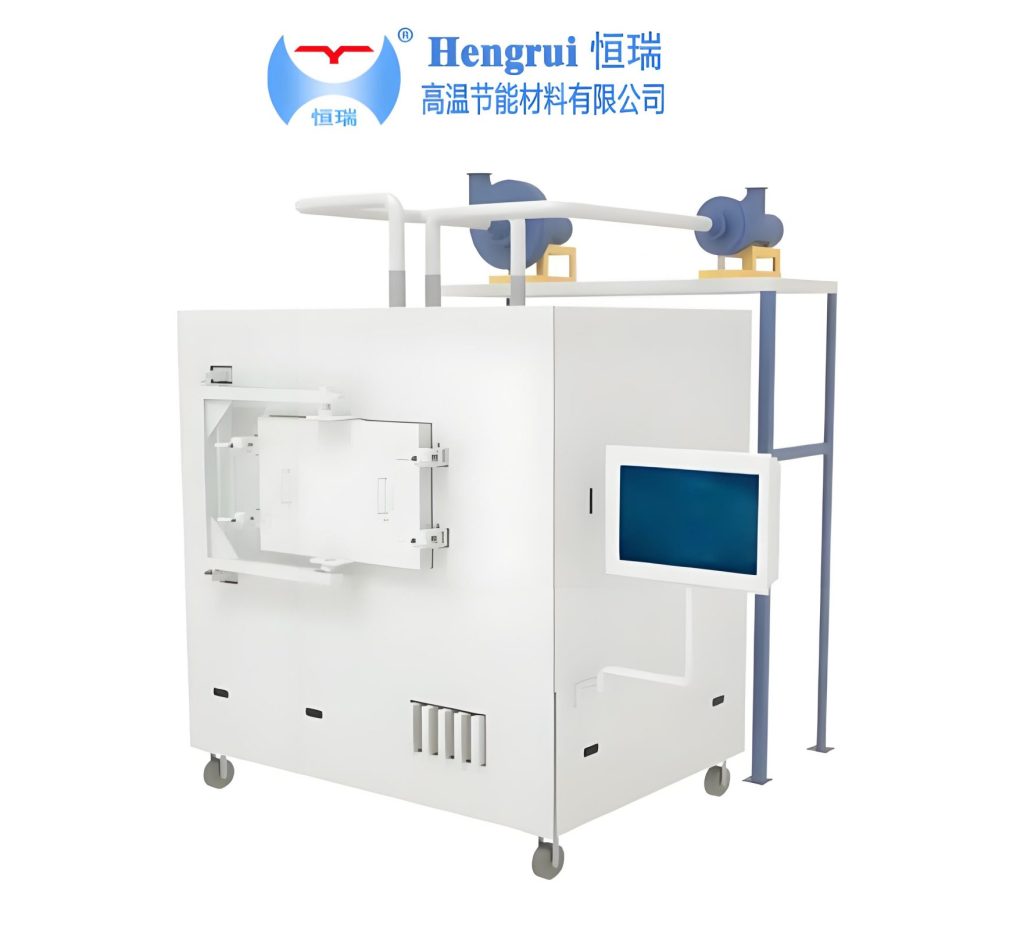
In the manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries, especially during the production of cathode and anode materials, the sintering or calcination process is one of the most critical steps. This process requires precise temperature control, uniform heat distribution, and effective insulation. As the industry moves toward higher energy efficiency and product consistency, ceramic fiber boards have become an essential material. They are used for furnace insulation, lining, and thermal management in sintering kilns used for electrode material production.

During the sintering of lithium-battery electrode materials such as lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄), NMC, and LCO, the working temperature often ranges from 800 °C to over 1000 °C. Ceramic fiber boards, made from high-purity aluminosilicate fibers, provide excellent resistance to high temperatures and maintain structural integrity under extreme thermal conditions. Their low thermal conductivity helps minimize heat loss and maintain stable internal furnace temperatures. This improves overall energy efficiency and protects furnace components.
Uniform heat distribution is essential for producing consistent and high-quality electrode materials. Uneven temperatures inside the furnace can lead to partial sintering, degraded material performance, or increased waste.
Ceramic fiber boards provide excellent thermal shock resistance, allowing them to handle rapid temperature fluctuations without cracking or deformation. This ensures a more stable temperature field within the kiln and improves the quality uniformity of sintered materials.
Compared with traditional refractory bricks, ceramic fiber boards are lightweight and easy to handle, which significantly reduces the structural load on the furnace and simplifies installation. Their low heat storage capacity also allows for faster heating and cooling cycles, reducing production time and improving overall process efficiency.
By effectively reducing heat loss and maintaining higher internal temperatures with less energy, ceramic fiber boards help lower operational energy consumption. This results in lower production costs and aligns with modern manufacturing goals for sustainability and carbon reduction.
Furnace Wall and Roof Insulation
Used as hot-face and backup insulation layers to maintain high internal temperatures while keeping the furnace shell cool, thus extending equipment service life.
Support and Isolation Boards
Ceramic fiber boards can be used to support powder materials or trays during sintering. This prevents contamination from metal components and ensures product purity.
Temperature-Control Zones
In multi-zone sintering kilns (preheating, sintering, cooling), fiber boards are used to isolate temperature zones and stabilize transitions. This ensures consistent material processing conditions.
Furnace Retrofit and Energy Upgrades
Many existing sintering systems can be upgraded by replacing heavy refractory insulation with ceramic fiber boards. This effectively reduces shell temperature, improves thermal uniformity, and extends service intervals.
Energy Saving – Low thermal conductivity and reduced heat loss improve furnace efficiency and lower fuel or power costs.
Improved Product Quality – Stable temperature profiles ensure consistent sintering and optimized crystal structures for better electrochemical performance.
Reduced Maintenance Time – Lightweight and modular boards are easy to replace, minimizing downtime.
Extended Furnace Life – Reduced thermal stress prevents damage to the furnace shell and structural components.
Clean Operation – Ceramic fiber boards are chemically inert and non-polluting, maintaining a clean environment required for advanced battery material production.
When selecting ceramic fiber boards for lithium-battery material sintering applications, the following parameters should be evaluated:
Proper material selection ensures optimal insulation performance, mechanical durability, and long-term cost effectiveness in electrode sintering systems.
As the lithium-ion battery industry continues to evolve, the requirements for precision, energy efficiency, and equipment reliability become increasingly demanding. Ceramic fiber boards offer a comprehensive insulation solution that meets these modern standards. Their combination of high temperature resistance, excellent insulation, and superior thermal shock performance makes them a crucial component in the sintering of lithium-battery cathode and anode materials.
By integrating ceramic fiber boards into furnace designs, manufacturers can achieve significant improvements in energy efficiency, product consistency, and operational stability. This ultimately enhances both productivity and sustainability in the lithium battery supply chain.