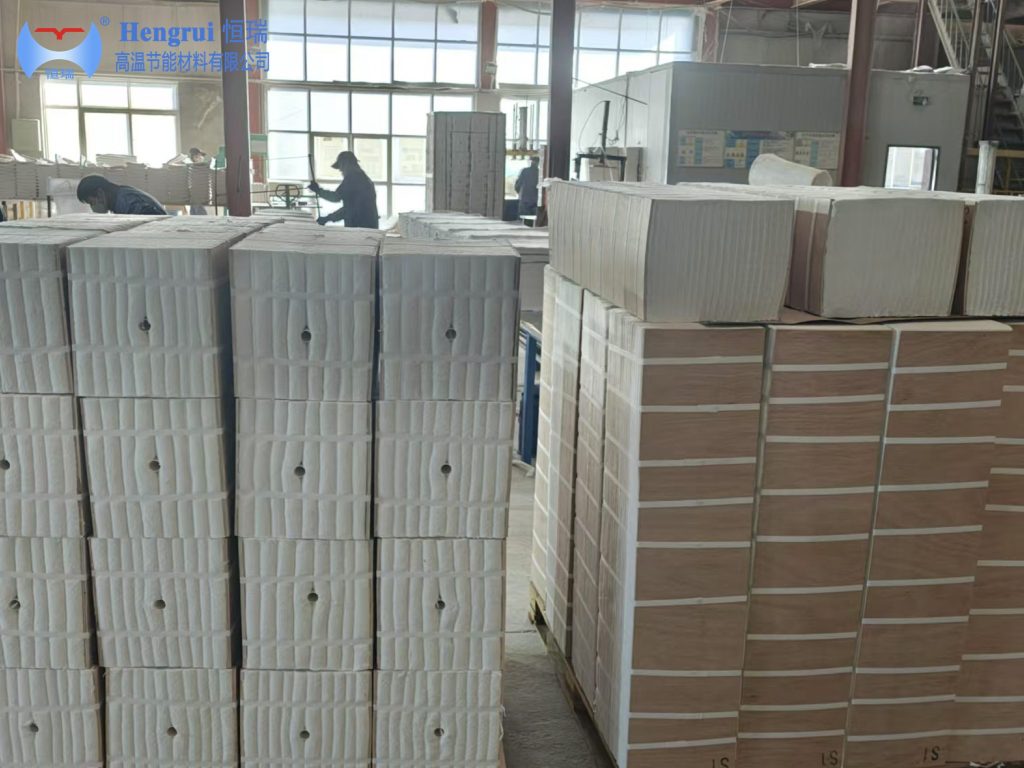
Ceramic fiber modules are widely used in the heat treatment industry due to their excellent high-temperature insulation, structural stability, and energy-saving properties. Below is a detailed exploration of how ceramic fiber modules are applied in various heat treatment furnace scenarios. Moreover, it explores why they are increasingly chosen as a superior lining material.

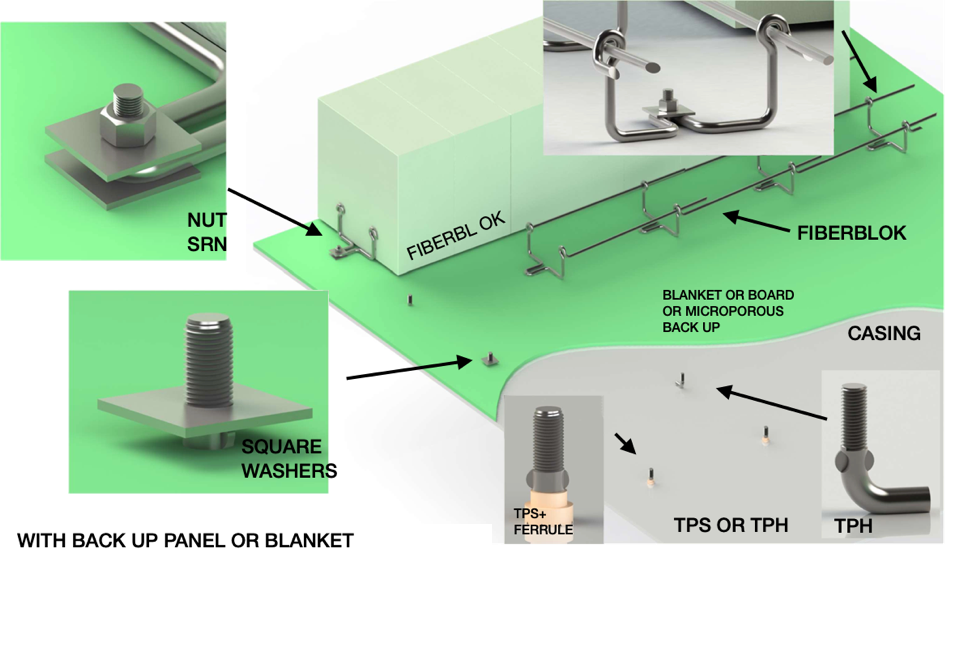
1.1 Annealing, Normalizing, and Quenching Furnaces
In annealing, normalizing, and quenching furnaces, ceramic fiber modules are used as a primary lining material. They help reduce heat loss, ensure temperature consistency, and improve energy efficiency. Compared to dense refractory bricks, fiber modules are lighter. They provide faster heating and cooling cycles, which is particularly beneficial in cyclic or intermittent operations.
1.2 Insulation Backup Layer
Ceramic fiber modules are often used as a backup insulation layer behind bricks or other lining materials. This multi-layer structure lowers the wall’s heat storage capacity. It accelerates thermal response and improves insulation, while also reducing stress on the outer shell of the furnace.
1.3 High-Temperature and Rapid Cycling Environments
For high-temperature or rapid cycling furnaces, such as those used in aggressive heat treatment cycles, modules rated for very high service temperatures (e.g., 1430 °C) are available. These modules maintain integrity under thermal stress. They are effective even under repeated heating and cooling cycles.
| Benefit | Explanation |
| Lightweight & Low Thermal Mass | Reduces the furnace’s overall weight and lowers its heat storage, enabling faster heating and cooling. |
| Excellent Thermal Shock Resistance | The fiber structure absorbs thermal stress, reducing the risk of cracks or spalling. |
| Energy Savings | High insulating efficiency and tight fit reduce energy usage during operation. |
| Easy Installation & Maintenance | Modular design allows for quick installation and replacement. |
| Compensation for Structural Movement | Elastic modules can adapt to furnace shell deformation, preserving tight thermal contact. |
To maximize performance, selecting the right ceramic fiber module requires careful consideration of several parameters:
In highly reducing atmospheres (e.g., hydrogen), ceramic fiber modules may suffer structural degradation over time. Therefore, they are often used as a secondary insulating layer rather than exposed directly to the flame or atmosphere.
While fiber modules are very effective as insulation, they may not offer the mechanical abrasion resistance or load-bearing capabilities of dense refractory bricks. Consequently, their placement in the furnace layout needs to be strategic.