Ceramic fiber blankets are essential high-temperature insulation materials widely used across the ceramic manufacturing industry. Their excellent thermal stability, low thermal conductivity, light weight, and strong resistance to thermal shock make them ideal for modern ceramic kilns and related thermal equipment. Today, ceramic fiber insulation has become one of the most effective replacements for traditional refractory bricks, helping manufacturers achieve higher energy efficiency, better temperature control, and longer equipment service life.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of how ceramic fiber blankets are used in different types of ceramic kilns and high-temperature systems.
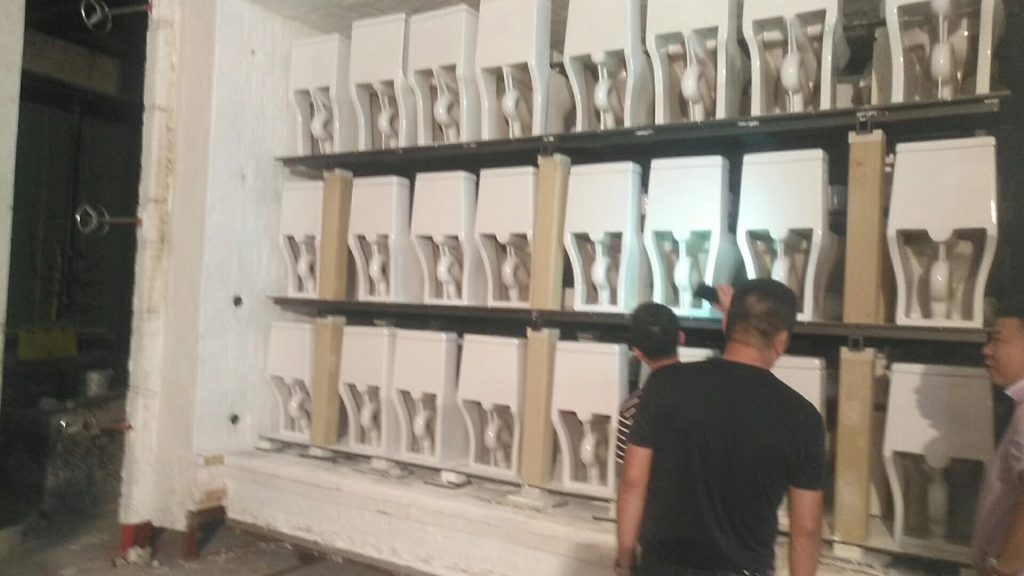

One of the most common applications of ceramic fiber blankets is as the insulation layer in ceramic kilns such as:
Ceramic fiber blankets significantly reduce heat loss by providing a high-performance thermal barrier on kiln walls, roofs, kiln cars, and furnace doors.
Key benefits:
Because the blanket material is elastic and flexible, it effectively fills gaps and compensates for expansion, improving kiln sealing performance and minimizing air leakage.
Ceramic kilns operate at extreme temperatures, causing structural expansion and the formation of gaps that must be tightly sealed.
Ceramic fiber materials—including loose fiber, blanket strips, and braided rope—are widely used for:
These sealing materials prevent heat leakage, protect structural steel components, and maintain stable kiln atmosphere.
Ceramic fiber blankets are often used as backup insulation behind refractory bricks or fiber modules.
This combined structure increases overall thermal resistance while reducing the thickness of the kiln wall.
Advantages of using ceramic fiber as backup insulation:
The low heat capacity of ceramic fiber also helps accelerate the firing cycle in fast-firing kilns.
Modern energy-efficient ceramic kilns increasingly use full-fiber linings, where the kiln wall and roof are built entirely using ceramic fiber modules and blankets.
Compared with traditional brick linings:
Full-fiber kilns enable rapid startup, improved firing efficiency, and lower energy usage—ideal for manufacturers seeking high output with reduced operating costs.
Ceramic fiber can be processed into lightweight kiln furniture such as:
These fiber-based components reduce heat absorption during firing, enabling:
Reduced load on kiln cars and structures
Shorter firing cycles
Lower fuel consumption
Improved thermal efficiency
Due to its ease of cutting, shaping, and installation, ceramic fiber blanket is often used for:
It provides fast, reliable thermal protection without requiring full rebuilds.
Suitable for kilns operating from 1000°C to 1400°C depending on grade.
Minimizes heat loss and delivers superior insulation efficiency.
Reduces total kiln weight and structural stress.
Withstands rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking.
Fits curved, irregular, or complex kiln surfaces with ease.
Lower operating costs and shorter firing cycles compared with brick linings.
Ceramic fiber blankets play a vital role in modern ceramic production. Whether they are used as sealing material, backup insulation, main refractory lining, kiln furniture, or high-temperature protection, ceramic fiber provides a superior combination of performance, efficiency, and durability.
Its advantages—lightweight structure, low thermal conductivity, fast installation, and excellent thermal shock resistance—make ceramic fiber blankets an essential material in today’s ceramic industry.