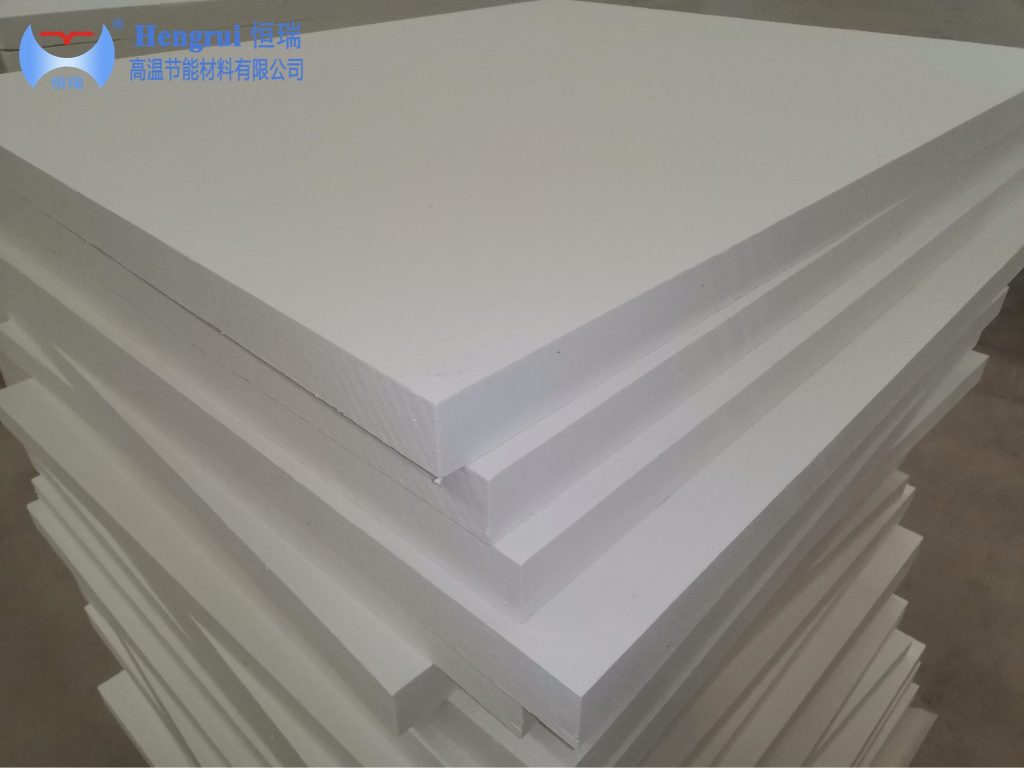
With the advancement of the electronics industry towards high-end and precision development, electronic kilns, as core thermal processing equipment in semiconductors, new energy materials, electronic ceramics, and other fields, are facing higher requirements for temperature uniformity, energy consumption control, and process stability. As a result, Fiber Board ceramic fiber boards, known for their lightweight, low thermal conductivity, and thermal shock resistance, are gradually replacing traditional refractory materials, becoming a key material for energy-saving retrofits in electronic kilns. This article analyzes the application scenarios, effectiveness, and development prospects of ceramic fiber boards in specific kiln types such as HTCC, MLCC, DBC sintering furnaces, and mesh belt furnaces.
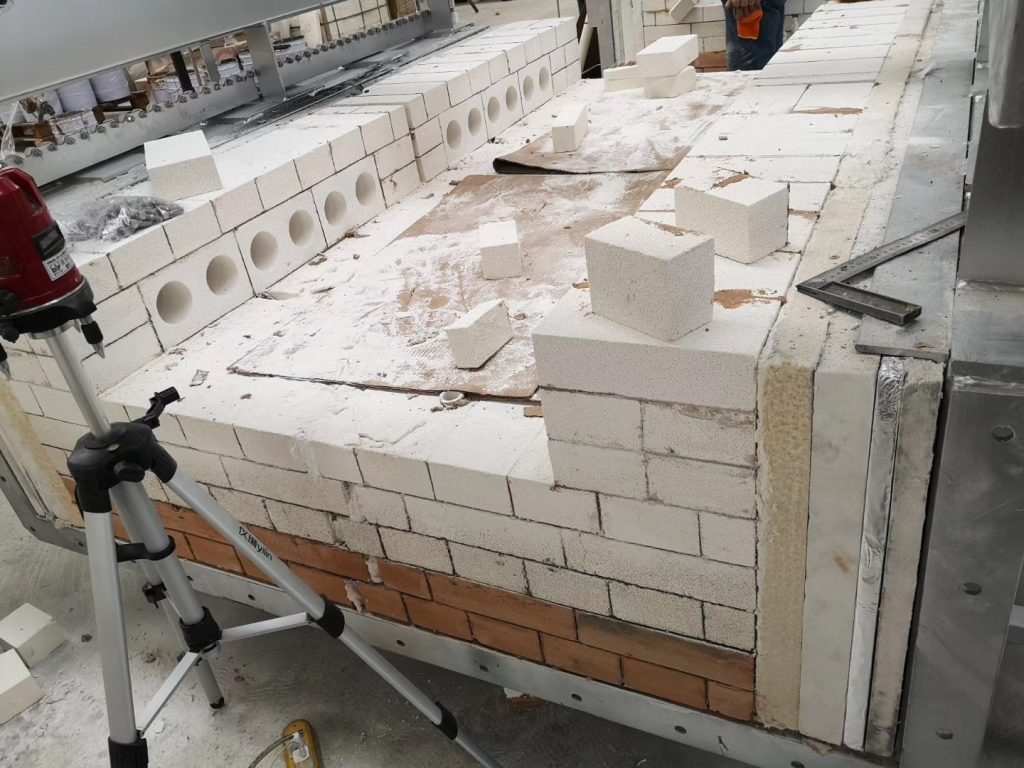

Ceramic fiber boards are rigid insulation materials made primarily from ceramic fibers through a wet vacuum forming process, offering the following core advantages:
Lightweight and Low Heat Storage: Density is only 1/5 to 1/10 of traditional refractory materials, significantly reducing the structural load on kilns and enabling lightweight equipment design.
Low Thermal Conductivity: Effectively blocks heat transfer, reducing heat loss, with energy savings exceeding 30%.
Excellent Thermal Stability: Resists rapid heating and cooling, with strong thermal shock resistance, suitable for the frequent start-stop requirements of electronic kilns.
Easy Installation: Customizable sizes and shapes, installation efficiency improved by over 50%, supporting the construction of complex furnace structures.
1. HTCC (High-Temperature Co-fired Ceramic) Sintering Furnaces
HTCC technology is widely used in high-reliability electronic packaging for aerospace, 5G communication, and other fields, with sintering temperatures reaching 1500–1650°C. As a lining material, ceramic fiber boards enhance process performance in the following ways:
2. MLCC (Multi-layer Ceramic Capacitor) Sintering Furnaces
As core components of electronic devices, MLCCs place extremely high demands on the cleanliness and temperature precision of sintering furnaces. The application of ceramic fiber boards includes:
3. DBC (Direct Bonded Copper) Process Furnaces
The DBC process requires eutectic bonding of copper and ceramics (e.g., alumina) at 1065°C, with strict requirements for atmosphere control and cooling rates:
4. Mesh Belt Sintering Furnaces and Pusher Furnaces
In the batch sintering of electronic powder materials (e.g., magnetic materials, ceramic devices), ceramic fiber boards significantly improve the energy efficiency of continuous production:
Automation Compatibility: Compatible with mesh belt transmission systems (variable frequency speed regulation 0.1–5 m/min), ensuring stable workpiece conveyance and temperature uniformity (≤±5°C).
Based on the operating temperature and atmosphere environment of electronic kilns, ceramic fiber boards require targeted selection: