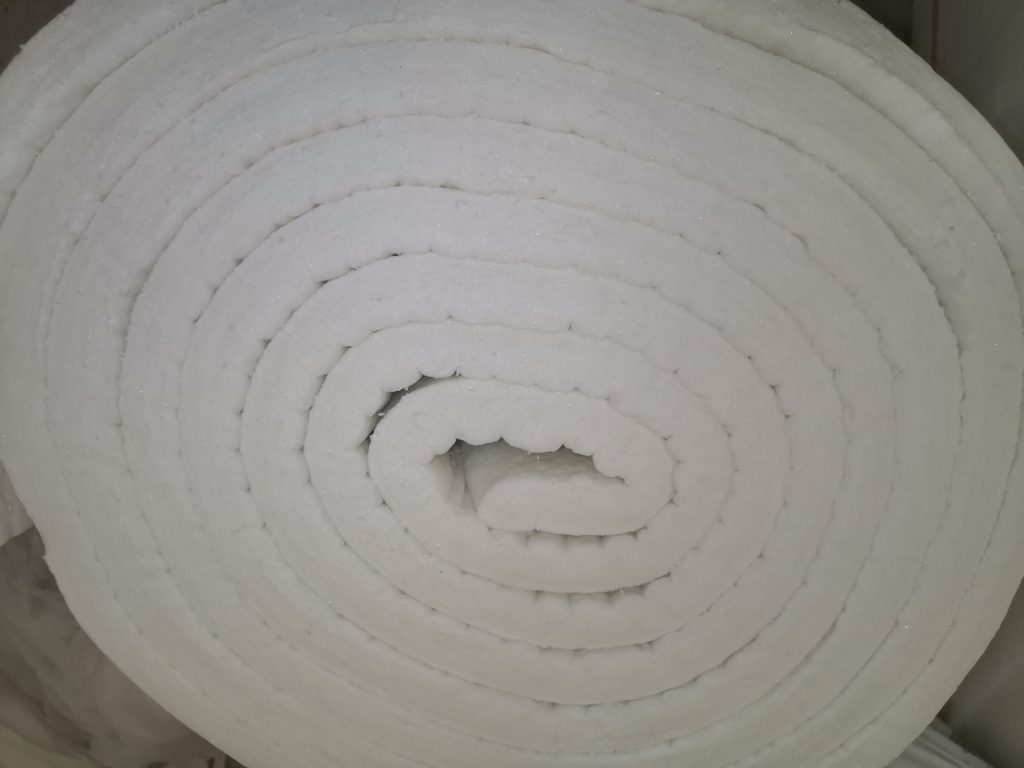
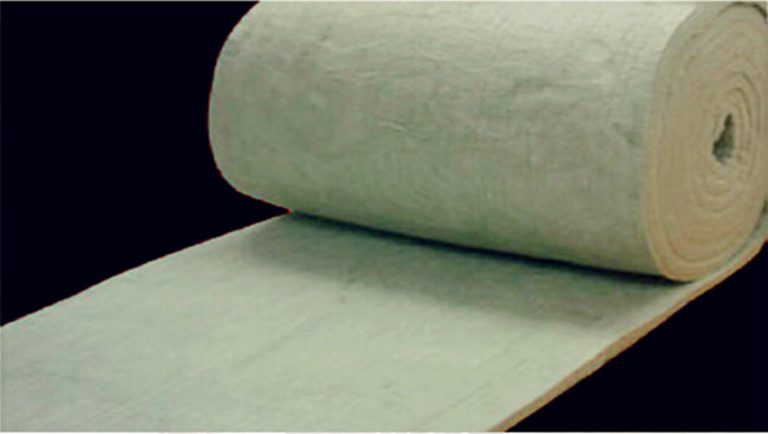
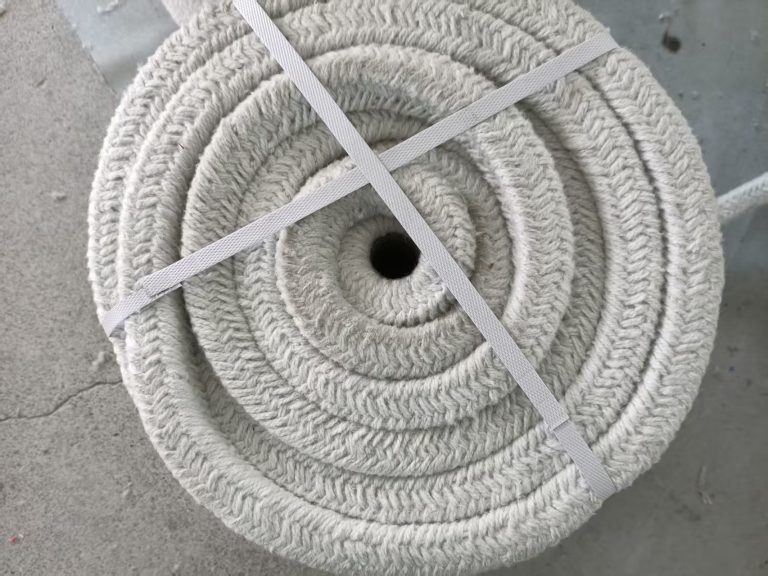
The ceramic fiber blanket is widely used in various industrial applications due to its excellent thermal insulation properties, high-temperature resistance, and lightweight nature. These ceramic fiber blankets are made from high-purity alumina-silica materials. This composition provides them with their unique characteristics. Let's delve into the composition of the ceramic fiber blanket and understand what makes these blankets so effective.
What is the Composition of Ceramic Fiber Blanket?
- Alumina (Al2O3): Alumina, or aluminum oxide, is a key component of ceramic fiber blankets. It typically constitutes around 45-55% of the blanket's composition. Alumina is known for its high melting point, excellent thermal stability, and resistance to chemical corrosion. These properties make the ceramic fiber blanket an ideal material for high-temperature insulation.
- Silica (SiO2): Silica, or silicon dioxide, is another major component of ceramic fiber blankets. It makes up about 45-55% of the composition. Silica provides the blanket with its fibrous structure and contributes to its thermal insulation properties. Furthermore, the presence of silica in the ceramic fiber blanket enhances its resistance to thermal shock and chemical attack.
- Other Oxides: In addition to alumina and silica, ceramic fiber blankets may contain small amounts of other oxides such as zirconia (ZrO2), titania (TiO2), and iron oxide (Fe2O3). These oxides are added to improve specific properties of ceramic fiber blankets. They increase resistance to high temperatures, enhance mechanical strength, and improve overall durability.
- Binder Materials: During the manufacturing process, binder materials are often added to ceramic fiber blankets to help hold the fibers together and improve their handling characteristics. These binders are typically organic compounds that burn off during the initial heating of the ceramic fiber blanket. This process leaves behind a strong and cohesive fibrous structure.
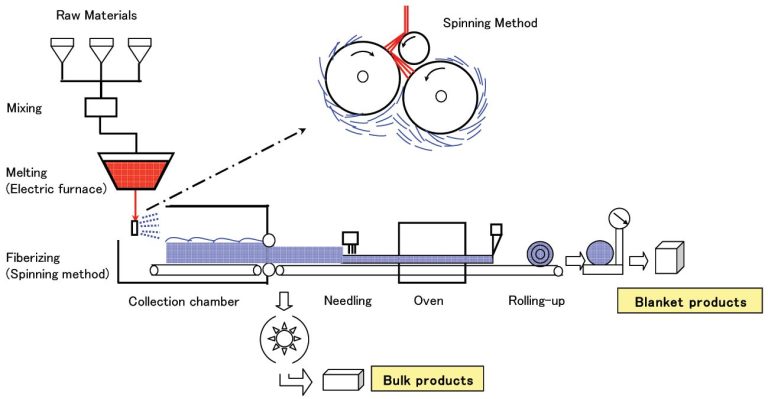
- Fiber Structure: The fibers in ceramic fiber blankets are typically produced through a process called "blown" or "spun" fiber production. In this process, molten alumina-silica material is blown or spun into fine fibers, which are then collected and formed into blankets. The resulting fiber structure is lightweight, flexible, and highly insulating. These are characteristics of a quality ceramic fiber blanket.
Conclusion: Ceramic fiber blankets are composed primarily of alumina and silica, with small amounts of other oxides and binder materials. This composition gives the ceramic fiber blanket its excellent thermal insulation properties, high-temperature resistance, and durability. These blankets are widely used in industries such as metallurgy, petrochemicals, and ceramics, where high-temperature insulation is crucial.