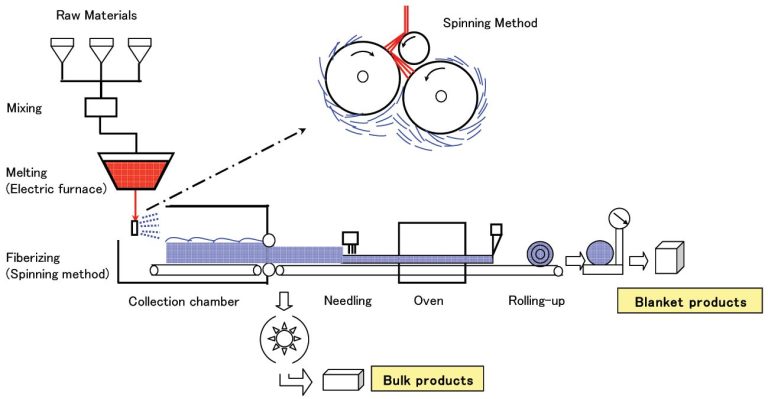
Introduction to Ceramic Fiber
Ceramic fiber, a lightweight refractory material composed of alumina-silicate。 Renowned for its exceptional thermal stability, low thermal conductivity, and resistance to thermal shock, is transforming kiln design, energy efficiency, and production workflows in the industry. This article explores its critical applications, advantages, and why it’s a game-changer for ceramic manufacturers worldwide.
Key Applications of Ceramic Fiber in the Ceramic Industry
1. Kiln and Furnace Linings
Ceramic fiber blankets, boards, and modules are widely used to line kilns and furnaces. Their low heat storage and high-temperature resistance (up to 1,400°C) ensure uniform heat distribution, reducing preheating time and energy consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional refractory bricks.
2. Thermal Insulation for Ceramic Processing
From drying chambers to tunnel kilns, ceramic fiber acts as a superior thermal barrier. Its lightweight nature minimizes structural load while maintaining consistent temperatures, critical for preventing cracks and defects in ceramic products like tiles, sanitaryware, and technical ceramics.
3. Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
By reducing heat loss, insulation slashes energy costs significantly. Studies show -lined kilns achieve 20-40% higher energy efficiency, making them ideal for sustainable manufacturing practices.
4. High-Temperature Filtration
filters capture particulate matter in kiln exhaust systems, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Their durability in corrosive environments extends filter lifespan, lowering maintenance costs.
- Enhanced Durability: Resists thermal cycling and chemical corrosion, extending equipment lifespan.
- Lightweight Design: Reduces kiln construction costs and simplifies installation.
- Eco-Friendly: Supports green manufacturing by lowering CO₂ emissions and energy use.
- Versatility: Adaptable to complex shapes and high-precision applications.