In the high-precision world of glass deep processing, thermal efficiency and structural integrity are the twin pillars of quality production. Among the various components of a glass tempering furnace, the Ceramic Fiber Roller Insulating Brick (often referred to as hole bricks or support blocks) plays a critical role. The role of ceramic fiber roller insulating bricks in glass tempering furnaces cannot be understated, as they are crucial for maintaining efficiency and integrity.

This article explores why these specialized ceramic components are indispensable for modern glass processing and how they contribute to superior tempered glass quality.
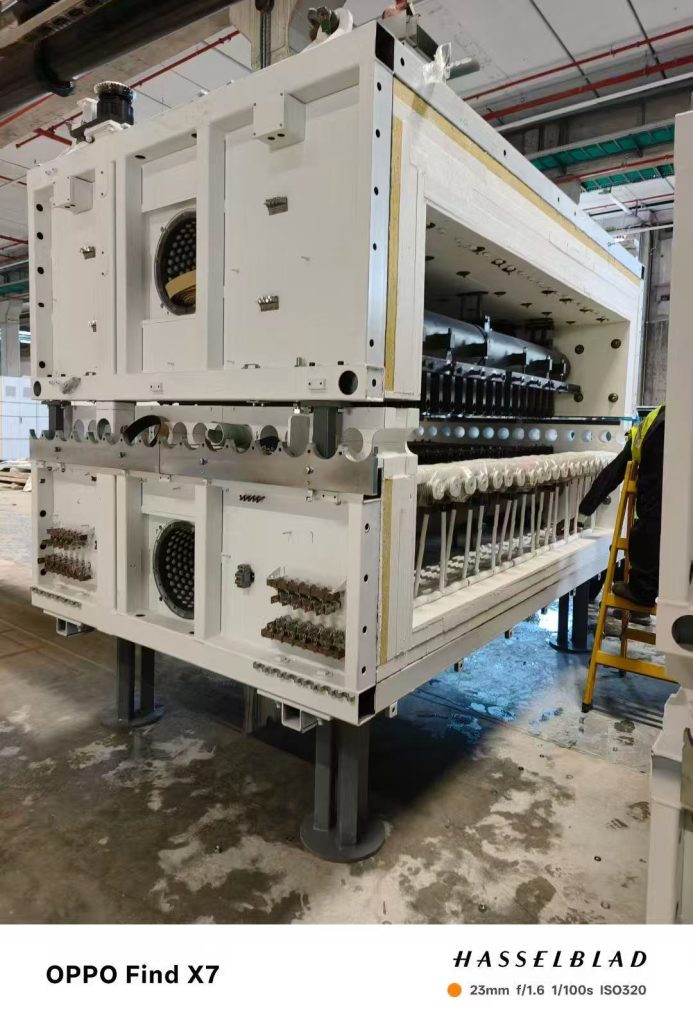
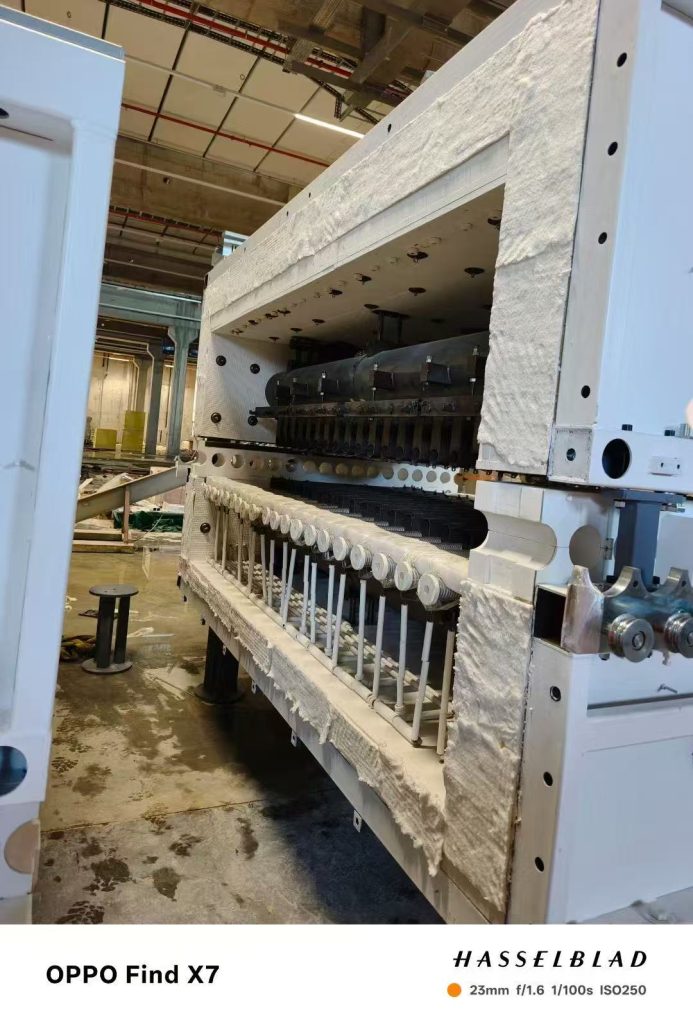


What are Ceramic Fiber Roller Insulating Bricks?
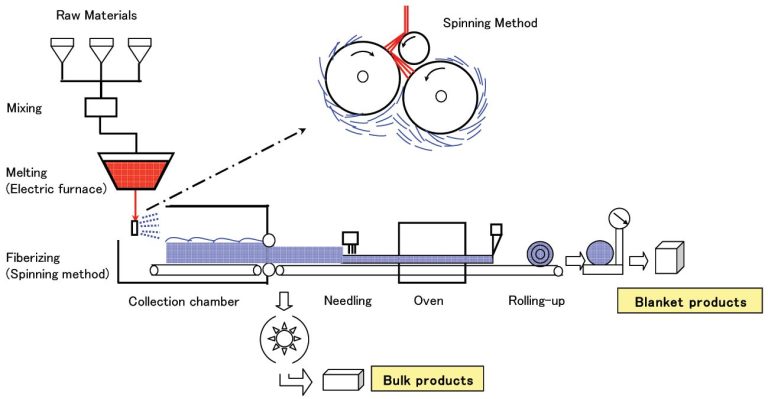
Ceramic fiber roller insulating bricks are high-temperature refractory components specifically designed to support the fused silica ceramic rollers in a tempering furnace. They are typically manufactured from high-purity alumina-silica fibers through a vacuum forming process, ensuring a lightweight yet robust structure.
Key Applications in Glass Tempering
In a glass tempering furnace, the heating chamber must maintain a stable environment, often exceeding 700°C. The insulating bricks are installed along the sides of the furnace to serve two primary functions:
Thermal Sealing: These bricks act as a thermal barrier between the high-temperature internal chamber and the external drive mechanism, preventing heat loss and protecting the furnace's outer casing
Roller Support & Alignment: They provide a precise seat for the ceramic rollers, ensuring they remain perfectly level. Any misalignment can lead to "roller waves" or optical distortion in the glass.
Advantages of Using Ceramic Fiber Materials
Choosing ceramic fiber over traditional heavy refractories offers several competitive advantages for glass manufacturers:
1. Exceptional Thermal Insulation
Ceramic fiber has extremely low thermal conductivity. By minimizing heat dissipation through the roller ports, furnaces can maintain a more uniform internal temperature, which is vital for the stress distribution during the quenching phase.
2. Low Heat Storage
Unlike dense firebricks, ceramic fiber bricks store very little heat. This allows for faster heating and cooling cycles, enabling manufacturers to adjust furnace settings quickly for different glass thicknesses (e.g., switching from 3mm to 12mm glass).
3. Thermal Shock Resistance
The tempering process involves rapid temperature fluctuations. Ceramic fiber bricks are highly resistant to thermal shock, meaning they won't crack or spall under sudden temperature changes, significantly extending the service life of the furnace lining.
4. Non-Contaminating Properties
High-quality ceramic fiber bricks are designed to be "dust-free." In glass processing, even the smallest particles can fuse onto the hot glass surface, causing "pitting" or surface defects. These bricks ensure a clean environment for high-end optical or architectural glass.