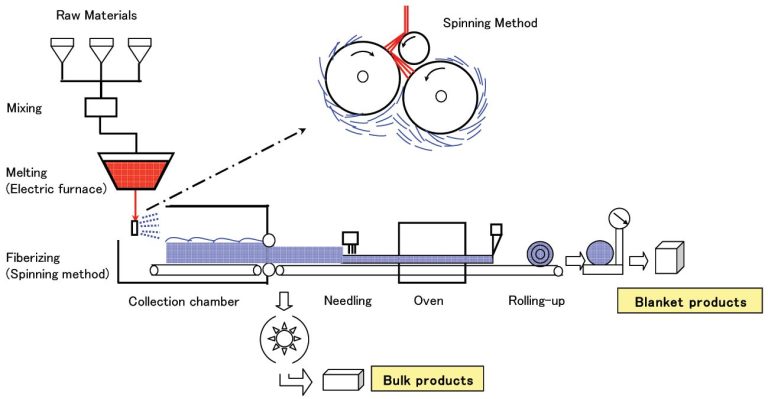
Polycrystalline mullite fibers and alumina fibers are widely used in the sintering of zirconia products in dental prosthetics furnaces. The fiber materials play a crucial role in these applications. This article will provide a detailed overview of the design and application of lining materials in dental sintering furnaces.

The primary role of polycrystalline mullite fibers and alumina fibers in dental sintering furnaces is for thermal insulation and heat preservation. Fiber structures effectively reduce heat loss within the furnace. This enhances the energy efficiency and overall performance of the sintering process. Furthermore, these fibers help in reducing thermal stress within the furnace, ultimately extending its lifespan. Polycrystalline mullite fibers are suitable for prolonged use at temperatures up to 1450 degrees Celsius. In contrast, alumina fibers can withstand temperatures up to 1650 degrees Celsius.
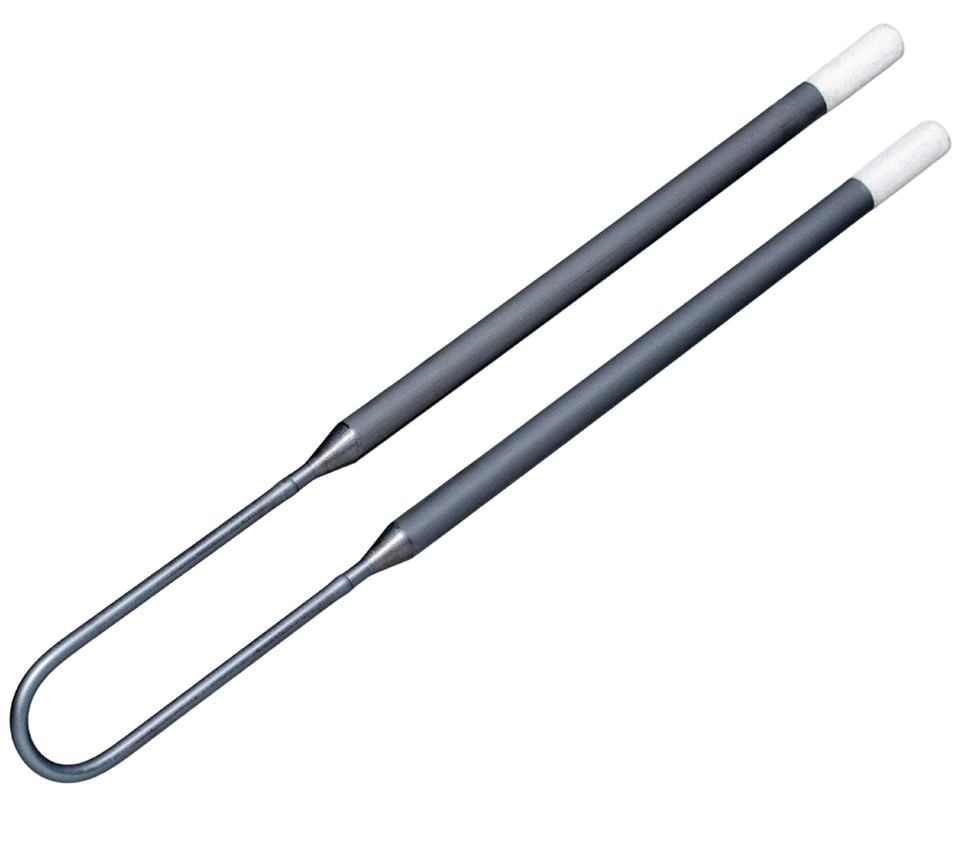

Moreover, these fibers aid in maintaining uniform temperatures within the furnace. This ensures the quality and stability of the dental sintering process. Fiber utilization plays a vital role. Therefore, the use of polycrystalline mullite fibers and alumina fibers is crucial in the sintering of dental prosthetics. This contributes significantly to its success and efficiency.