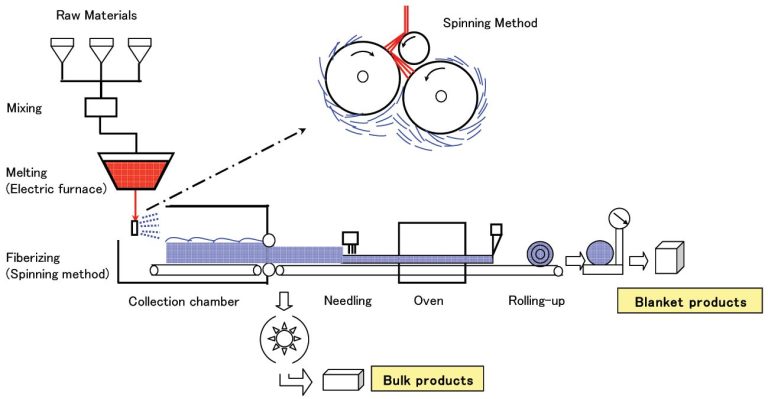
Introduction
Ceramic fiber modules are widely recognized for their excellent thermal insulation, structural stability, and energy-saving performance. They are commonly applied in industrial furnaces and thermal equipment, significantly reducing heat loss and improving operational efficiency.
However, in certain furnace environments, ceramic fiber modules cannot be used directly as the working layer that comes into contact with furnace gases. Instead, they are more suitable as insulating backup layers to enhance overall energy efficiency and prolong furnace service life.

Why Ceramic Fiber Modules Cannot Be Directly Used in Some Furnaces
When ceramic fibers are exposed to reducing or chemically reactive atmospheres, they undergo structural changes at high temperatures. Gases such as H₂, CO, NH₃, and CH₄ can accelerate:
- Crystallization rate of ceramic fibers
- Powdering (loss of structural integrity) at lower-than-expected temperatures
This results in fiber degradation, reducing the lifespan of the refractory lining and compromising furnace performance.
Furnace Types Where Ceramic Fiber Modules Should Be Used as Insulation Layers Only
Even when furnace temperatures fall within the 950°C–1250°C range, ceramic fiber modules should not serve as the working layer in the following conditions:
- Reducing Atmosphere Furnaces
- Examples: Carburizing furnaces, vacuum furnaces
- Reason: High levels of reducing gases weaken fiber structure.
- Furnaces with Protective but Non-Inert Gases
- Examples: Aluminum melting furnaces, wax-shell firing furnaces used in special casting
- Reason: Vapors released from heated workpieces chemically affect fiber integrity.
In these scenarios, ceramic fiber modules are best applied as a secondary insulation layer rather than the direct working surface.
Recommended Application Strategy
- To maximize performance and service life, ceramic fiber modules should be used in multi-layer furnace lining structures:
- Hot Face (Working Layer): Dense refractory bricks or castables resistant to chemical attack
- Backup Insulation Layer: Ceramic fiber modules, providing low thermal conductivity and energy efficiency
- This layered approach ensures:
- Enhanced thermal insulation
- Reduced fuel consumption
- Longer furnace operating life
Conclusion
Ceramic fiber modules remain an ideal insulation material for industrial furnaces due to their lightweight design, excellent insulation properties, and energy-saving benefits. However, in environments containing reducing or chemically reactive gases, they should be applied as non-working insulation layers to avoid premature degradation.
👉 Contact us today to learn more about optimized ceramic fiber module solutions for your furnace application.