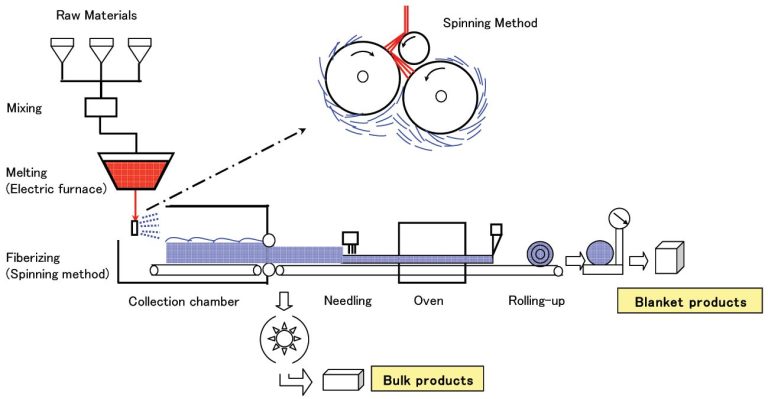
1. Introduction
Ceramic board insulation is a high-performance material widely used in industries requiring extreme temperature resistance and thermal stability. Composed of ceramic fibers bonded with inorganic binders, it combines lightweight properties with exceptional insulating capabilities. This article explores its characteristics, applications, advantages, and future trends.
2. Key Properties
- High-Temperature Resistance: Withstands temperatures up to 1600∘C1600∘C (2912∘F2912∘F), ideal for furnaces and kilns.
- Low Thermal Conductivity: Thermal conductivity ranges between 0.1–0.2 W/m\cdotpK0.1–0.2W/m\cdotpK, ensuring minimal heat transfer.
- Chemical Stability: Resists corrosion from acids, alkalis, and organic solvents.
- Mechanical Strength: Retains structural integrity under thermal cycling and mechanical stress.
3. Applications
- Industrial Furnaces: Lining for steelmaking, glass production, and petrochemical reactors.
- Aerospace: Thermal protection in rocket nozzles and spacecraft components.
- Construction: Fireproofing in high-rise buildings and energy-efficient insulation.
- Automotive: Heat shields in exhaust systems and engine compartments.
4. Advantages Over Traditional Insulation
- Energy Efficiency: Reduces heat loss by 30–50% compared to conventional materials.
- Space-Saving: Thin layers achieve equivalent insulation performance.
- Environmental Safety: Free from asbestos and harmful particulates.
5. Installation and Maintenance
- Precision Cutting: Customizable shapes using CNC machines or hand tools.
- Durability: Requires minimal upkeep, even in harsh environments.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Long lifespan offsets initial investment costs.